January 27, 2022 Leave a Comment 3D printed instruments are not a new thing, as we have seen with Olaf Diegel’s ever growing range of AM guitar creations. But most quality boutique instruments carry a price tag to match the effort of creation and the small scales of production. Enter musician/engineer Matthew Canel, who hopes to change that. Canel is an engineering graduate from Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio and in a previous life spent time learning the cello. Motivated by the high cost of musical instruments (cello in particular), Canel has turned to additive manufacturing to make instruments of a reasonable quality for students. The FDM printed violins are on sale via his 3DMusic website, and can be purchased for as little as $200. Two printed violins, just chillin on a bench. (Image credit: 3D Music LLC) That may sound a little expensive for an FDM print, but… read more
3D Printing
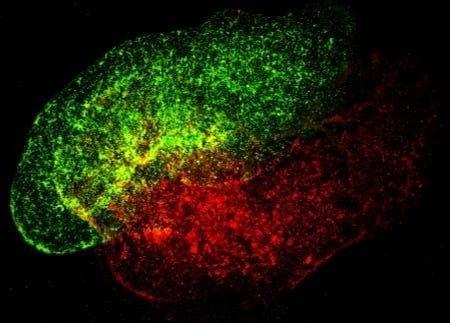
February 3, 2022 Leave a Comment It has been a while since we have covered anything in the domain of bioprinting. It’s not that we don’t like writing about bioprinting around here, but given the current state of technological readiness there is a very fine line between a 3D printed heart, and a 3D printed steak, functionally speaking. But bioprinting goes beyond simply just (eventually) printing large transplantable organs. The precision of the CNC guided bioprinting toolhead can deliver materials of various properties to make other biological systems too. And that is exactly what Prellis Biologics have been doing with their 3D printed lymph nodes, as revealed in a recent press release. Human immune cells in a printed lymph node (Image credit: Prellis Biologics) Prellis Biologics had previously dabbled in the realm of 3D printed organoids (such as kidneys) but have since shifted their expertise to smaller organoids such as… read more
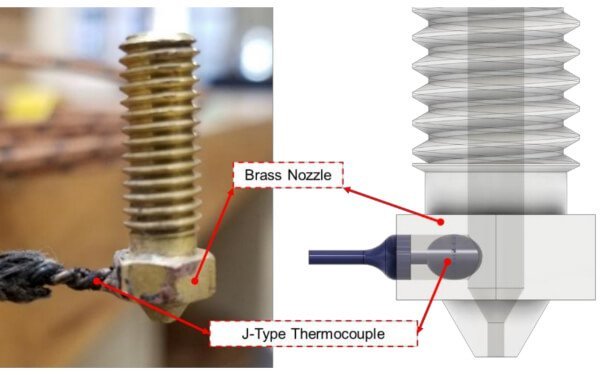
January 22, 2022 Leave a Comment In-situ monitoring of the status of feedstocks is a popular topic among researchers, regardless of the type of printer being used. Inroads are being made towards greater quality control and repeatability by use of various sensors in the printing process in both metal and plastic printing, and these technologies may very well end up in consumer products…especially if there isn’t too much expensive hardware involved. One team at Penn State University is carving one such inroad in the area of FFF printing, and they have published details about their research into computer vision aided filament measurement in the Manufacturing Processes and Systems section of the Materials journal. Using a microscope camera, an FFF printer and a whole bunch of code, researcher Rakshith Badarinath set about using computer vision to detect the width (and hence, volumetric flow rate) of the extruded filament as it was… read more
January 18, 2022 Leave a Comment IKEA, the Swedish purveyor of meatballs and rude-sounding flat-pack furniture products, has revealed their new range of 3D printed home decor items, which are currently being trialled with online customers in Germany. So far the product line features several decorative items manufactured with a triangular lattice style familiar to AM fans. IKEA has named this product line as “FLAMTRÄD”, which according to Google Translate, means “Flame Trees”. There is a distinct lack of fire or trees visible in the product line, as currently most of the items are in the form of human heads and hands. You can see the main item in the range in the image below, with its characteristic AM lattices giving the product its form. FLAMTRÄD : Kopf weiß. Also available in Kopf schwarz (Image credit: IKEA) To complement the printed heads on offer, the online store boasts a selection… read more
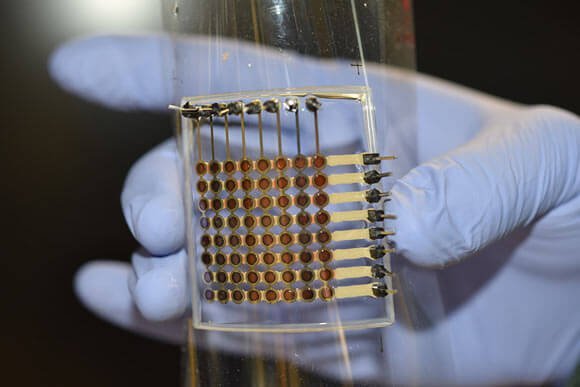
January 13, 2022 Leave a Comment OLEDs are traditionally manufactured using multiple substrates of various materials. The light comes from the emissive layer, which exchanges electrons for photons to produce light. The color of the light depends on the type of organic molecule in the emissive layer. Typically they are manufactured by various deposition processes and use inkjet printing to add the organic layers between the anode and the cathode before a final piece of glass or plastic is applied to complete the OLED display. If that sounds like a bit of a chore, then you are absolutely correct. That is why OLEDs are expensive devices. But a team of researchers from University of Minnesota Twin Cities have recently published a means to 3D print OLED panels, which could open the way for OLED panels to be manufactured in the home. You can see the 64 pixel (hand for scale)… read more